eiConsole v.25R1
Documentation
eiConsole Tutorial Basic
Routing Modules
In the eiConsole, Routing Modules are used to send a message to some subset of defined target systems. To configure a Routing Module, start by selecting and opening any existing interface. Next, double-click your interface to open the main route grid. Click the route icon in the main route grid and select the Routing Rules configuration tab.
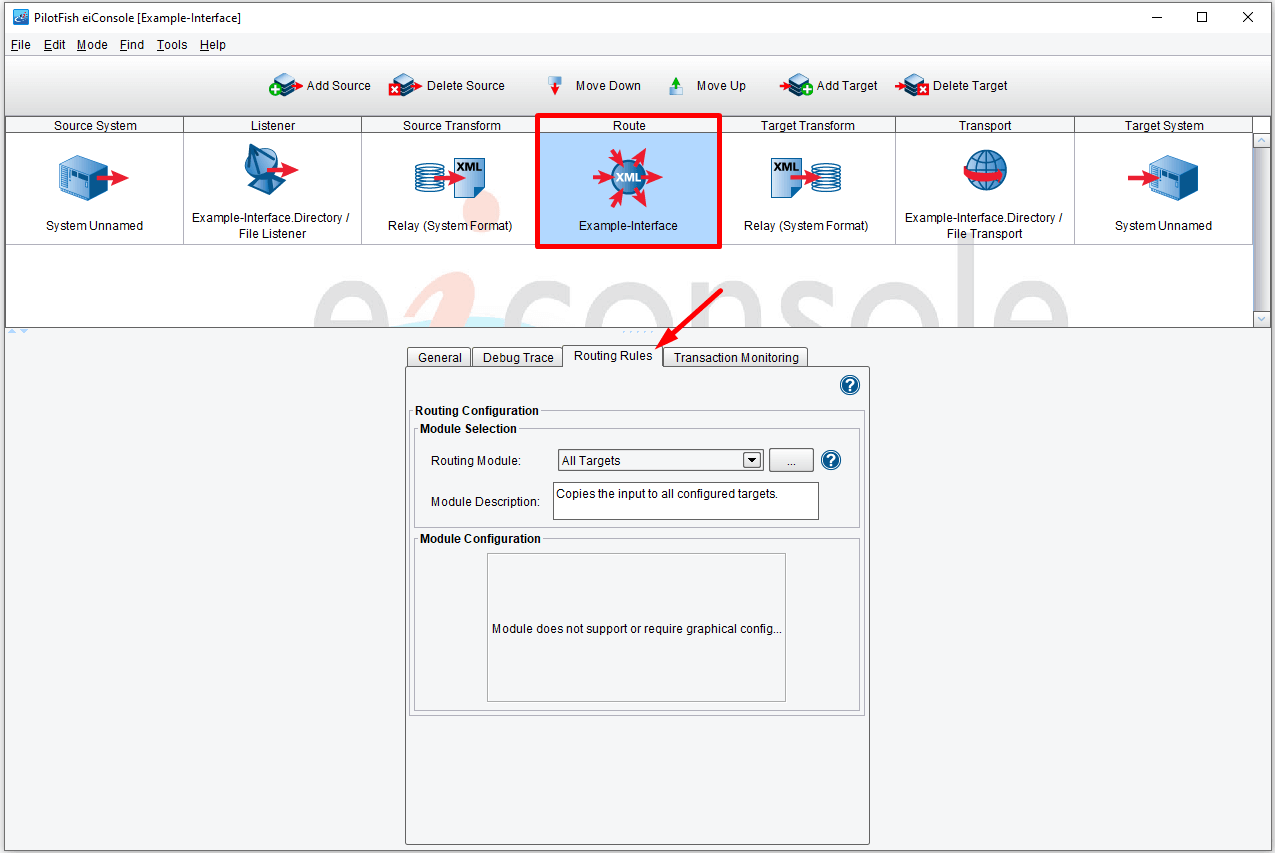
The eiConsole comes bundled with 3 out-of-the-box Routing Modules. The simplest of these and the default is the All Targets. This Module will take any inbound message and send it to each defined target system.
The second included Routing Modules is the Load Balancer Routing Module. It balances the load of the target Transports by successively calling all target systems. One target system is called for one transaction. Note: Some of the Transports may not work correctly with simultaneous connections or will be limited to some number of them.
The third routing module in the list is the XPath Routing Module. Most commonly, when you want to route a transaction to some subset of the defined target systems, you will use the content of the message or the metadata associated with the message to determine what data needs to be sent to which target systems. XPath is the most typical mechanism for querying this data.
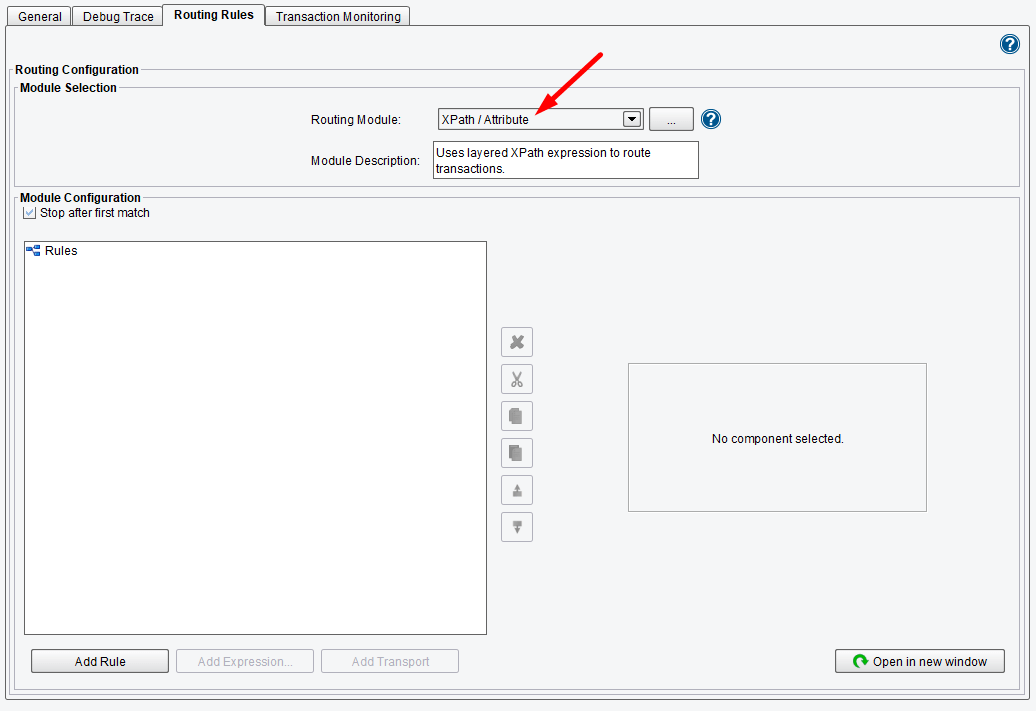
To configure an XPath based Routing Module, select XPath/Attribute from the Routing Module drop-down.
In the Module Configuration area, a tree will appear. At first, this tree will only contain a rules node.
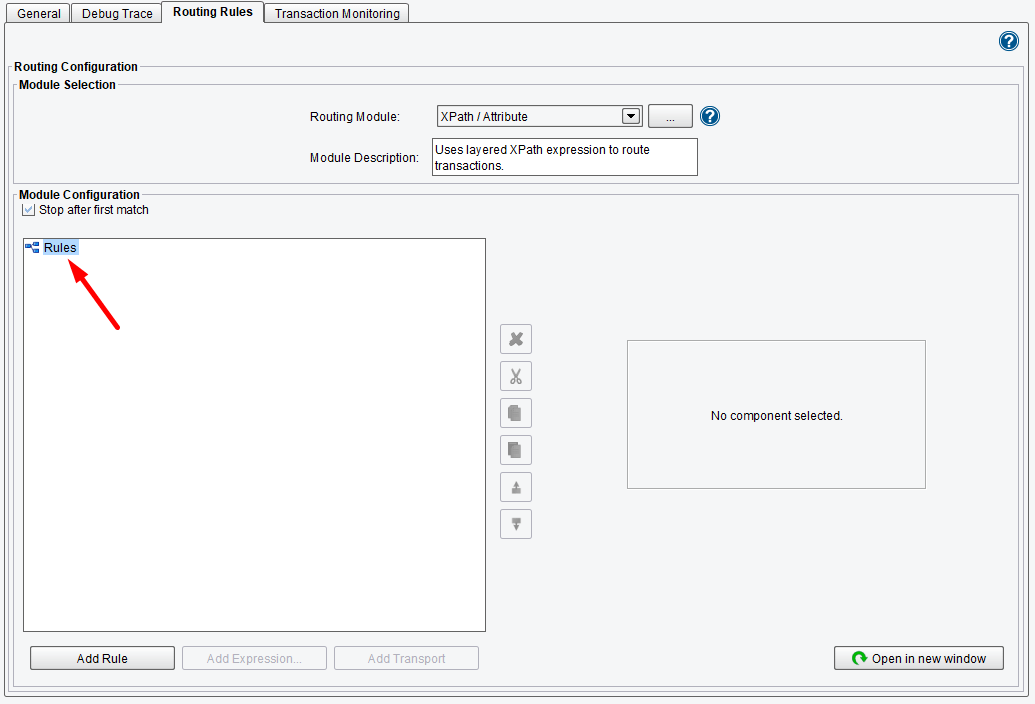
You will build this tree with all of the rules that you need to determine what information needs to be sent to which target systems. Select the Rules node by left-clicking and click on the Add Rule button to add a rule (or right-click on the node).
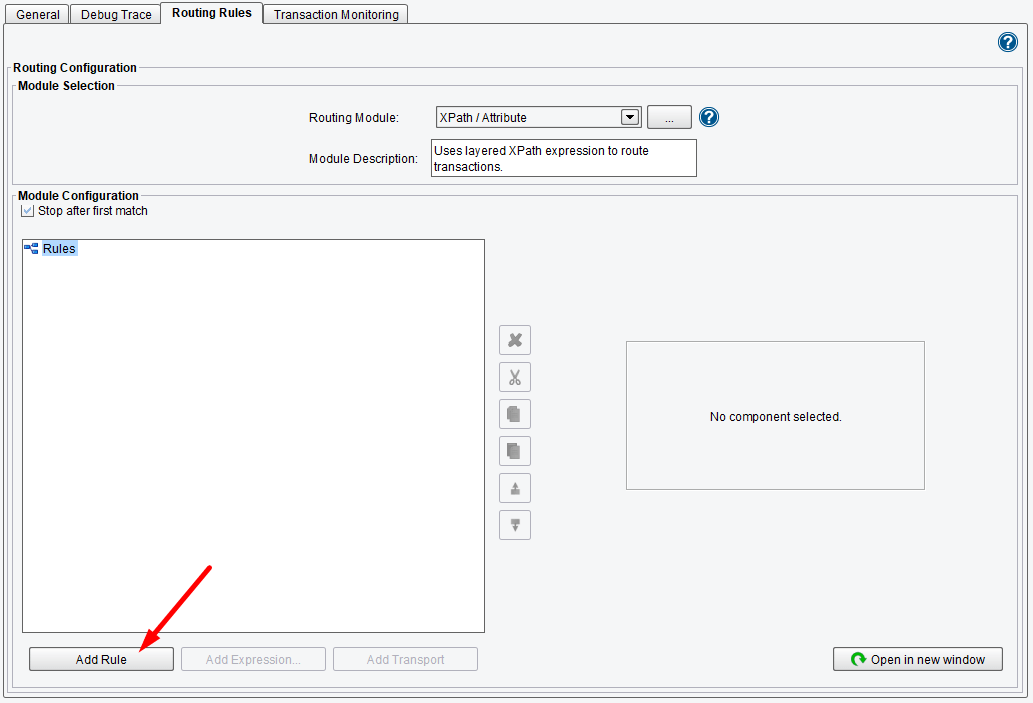
Click the Add Rule button.
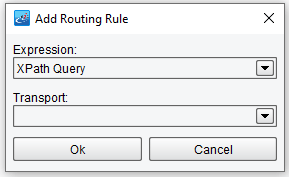
The Add Routing Rule dialog will appear.
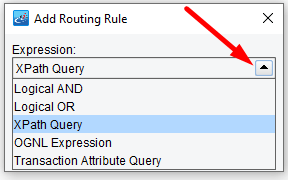
There are several ways to associate expressions with rules. Most commonly, you will use an XPath Query.
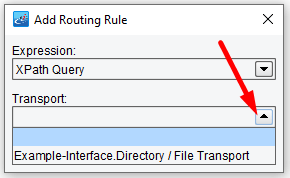
After XPath Query is selected from the drop-down menu, you will associate a Target System with this rule. Select Transport Target. You’ll be able to select from all of the fully configured Transports.
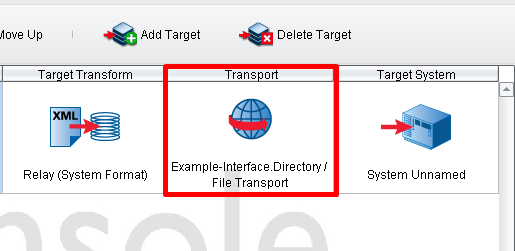
In our case, it is only Example-Interface.Directory Transport.
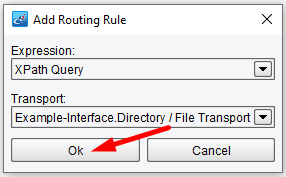
Click OK.
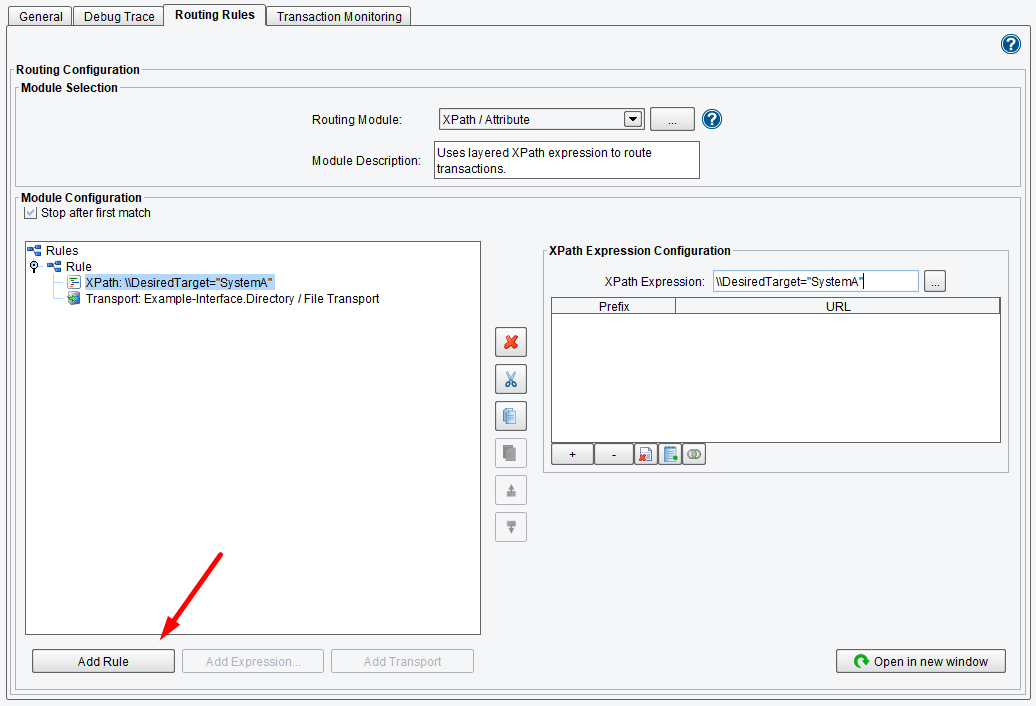
When XPath Query and Transport are selected, an XPath Expression Configuration dialogue will appear to the right. Here you will enter in the XPath Expression that you would like to evaluate. Enter \\DesiredTarget = "SystemA" in the dialogue panel. Once this information is entered, it will appear as an XPath node in the Module Configuration tree (left).
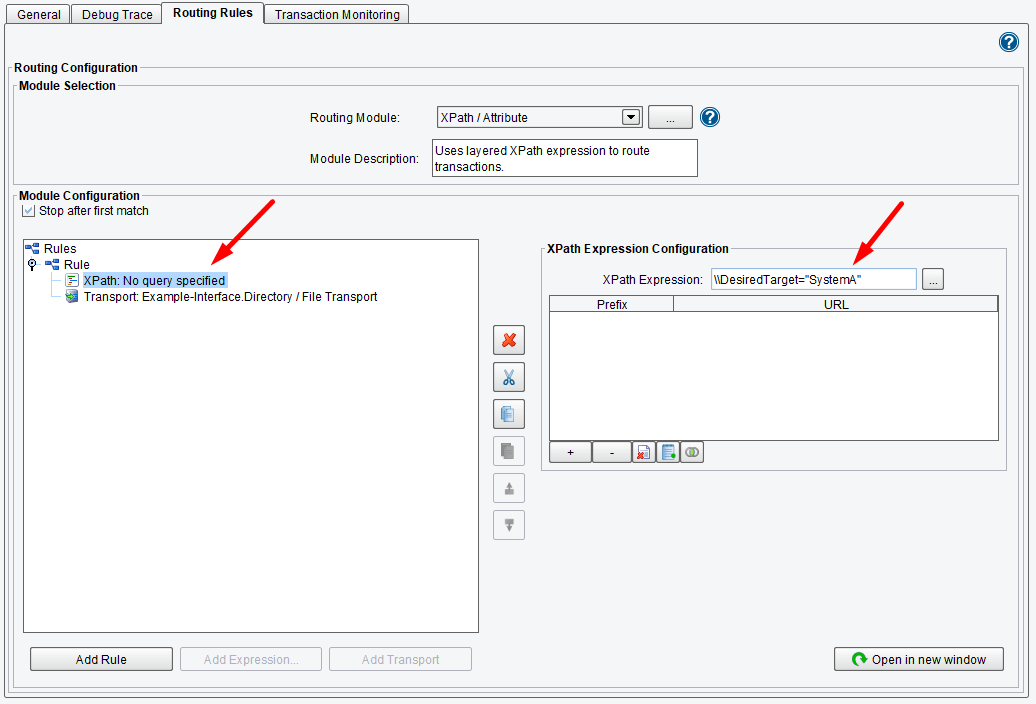
This Routing Module will execute any time that the Desired Target equals System A (as seen in the diagram below), and you will send the data along to this defined Transport.
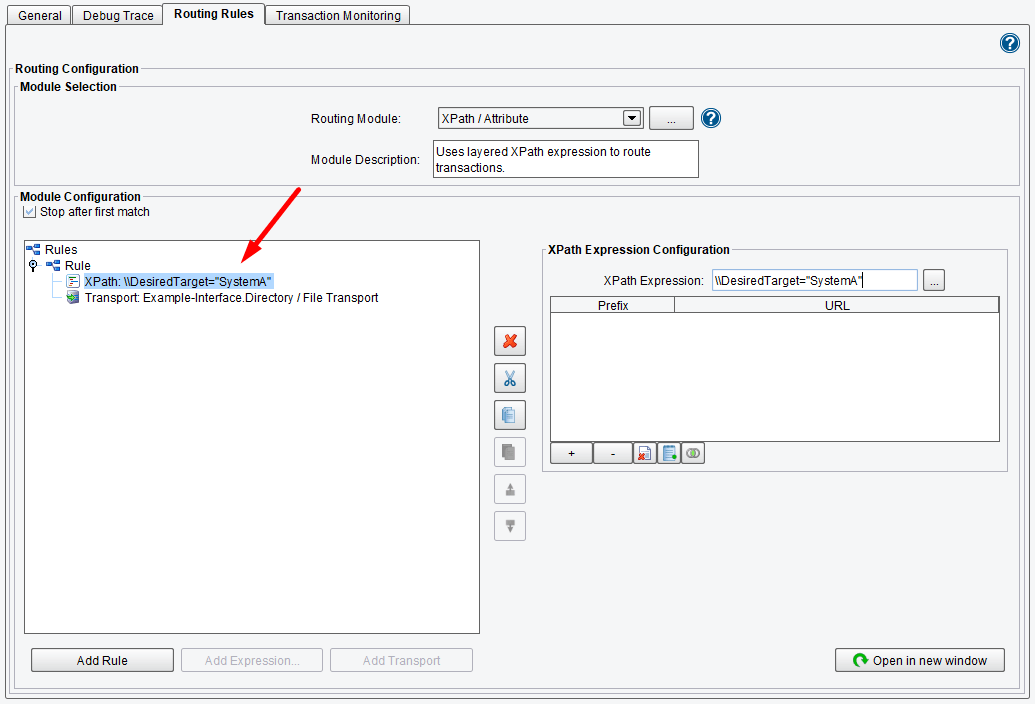
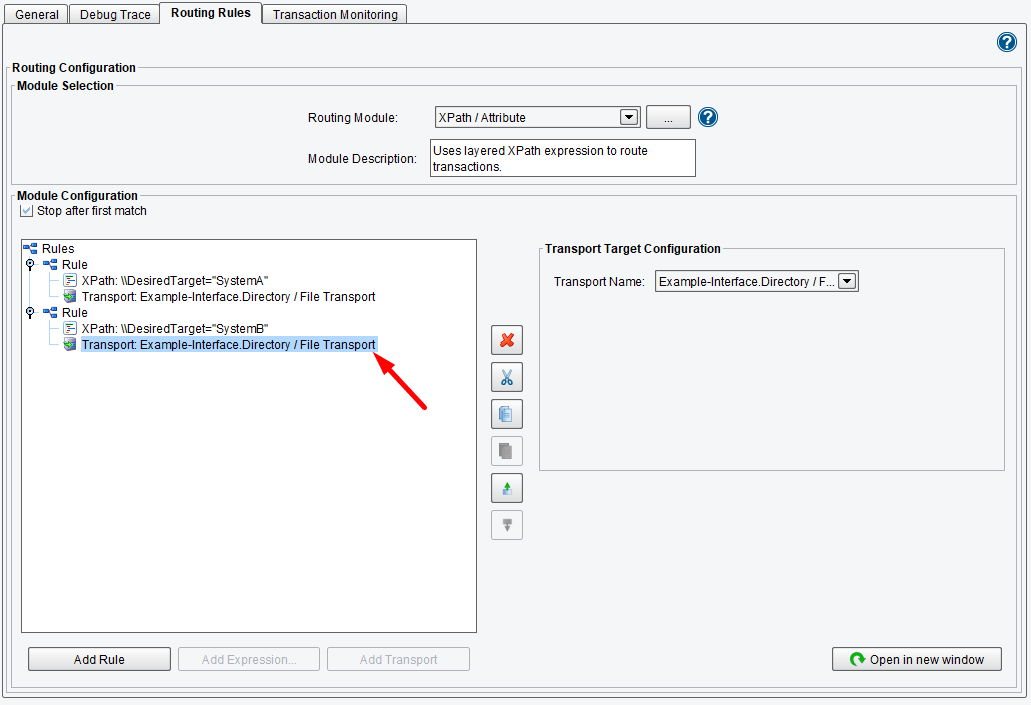
You can add additional rules by clicking the Add Rule button again (or right-clicking the Rules node) and continuing in the way you did before.
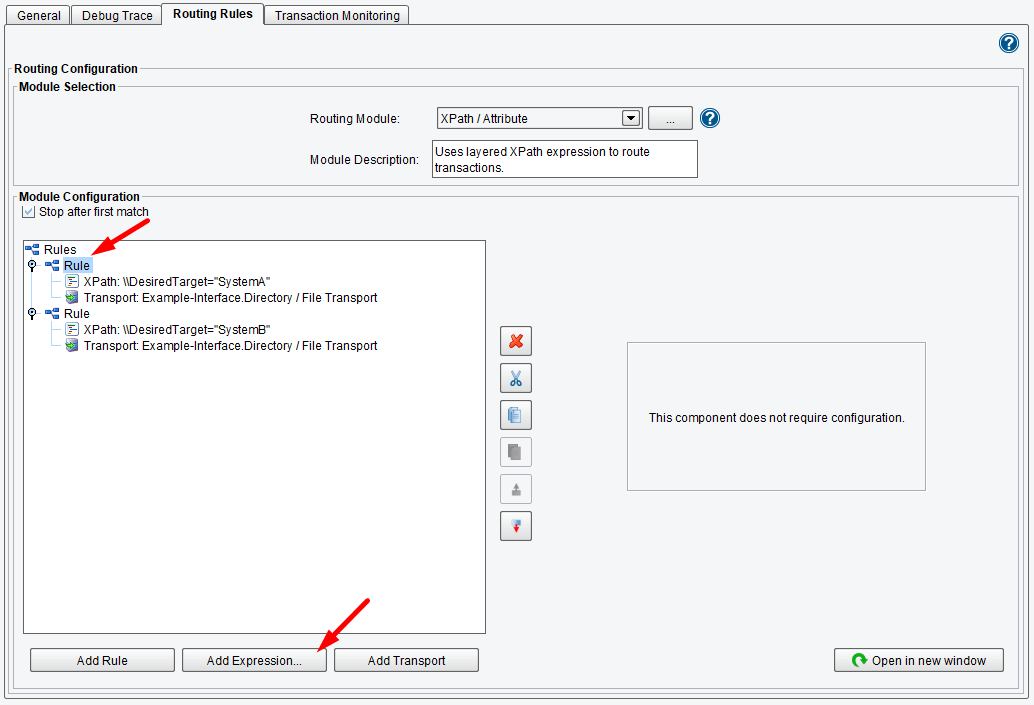
Rules can also be combined using Boolean operators. This can be done by clicking the Add Expression and selecting an expression type as a Logical AND or Logical OR rather than an XPath Query.
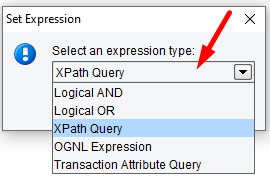
You can also query Transaction Attributes associated with a message using the Transaction Attribute Query option.
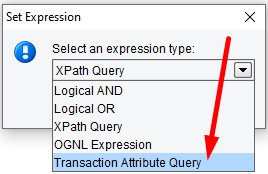
Attribute queries will allow you to inspect an Attribute associated with a transaction, apply an Operator and compare it to a particular Attribute value.
Rules can also be deleted and moved through the tree with control buttons (or right-click).
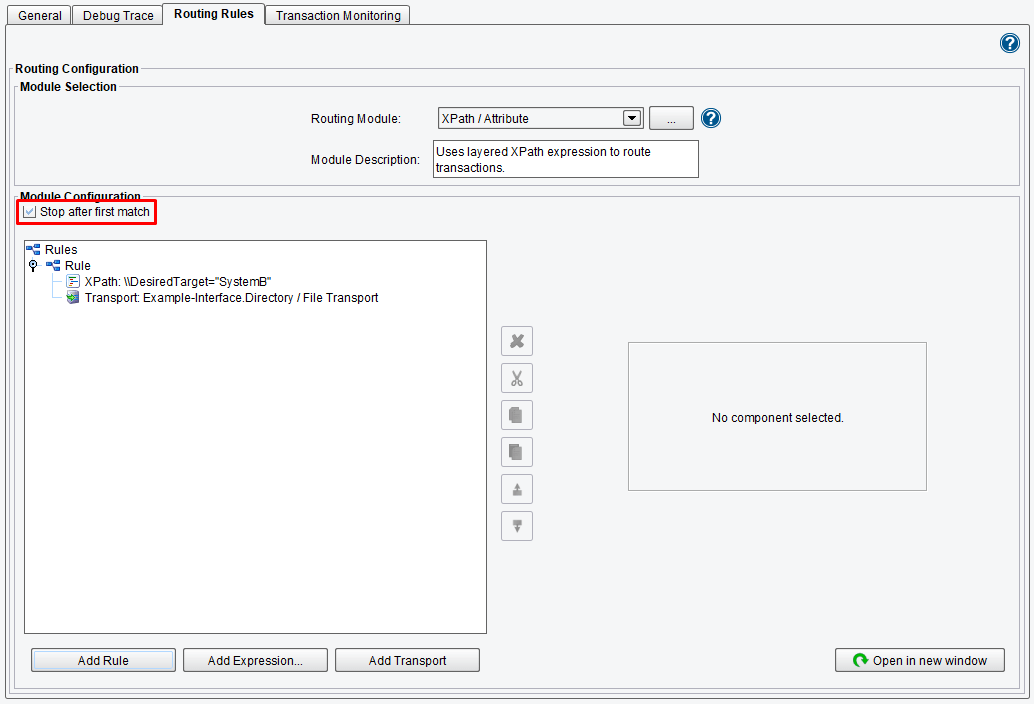
When the route node of the Module configuration tree is selected, you’ll see that you have the option to stop after the first match. If you wish to send the data to multiple target systems, you will want to uncheck this. This means that all XPaths will be evaluated and all XPaths that are returned true will have their Transports invoked. Only the first rule that returns true will be invoked when this is left checked and only that Transport will be used.
If you would like more information about using the eiConsole’s Routing Modules, please Contact Us
