HL7 Message Routing Using XPATH Expression
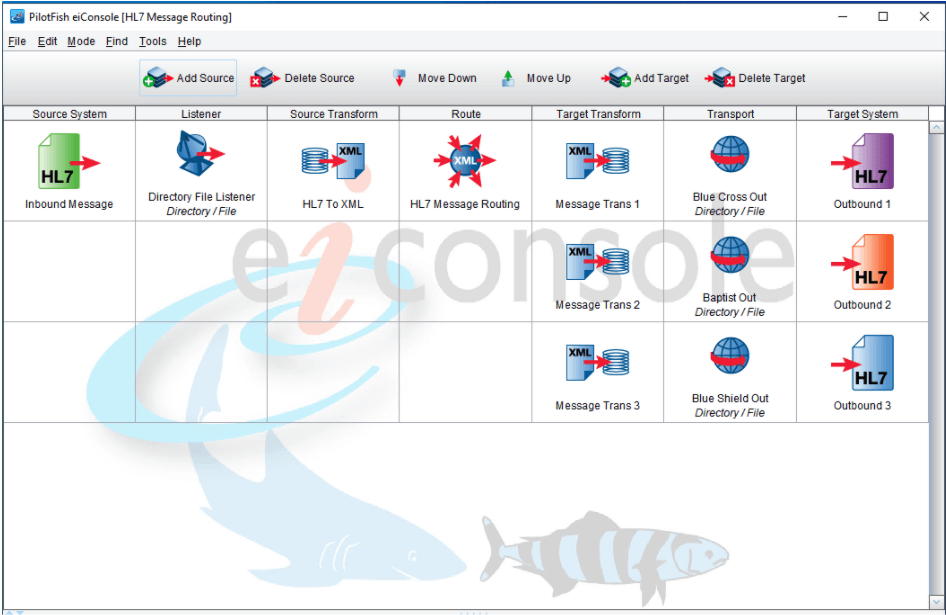
This route, ‘HL7 Message Routing’, receives an HL7 message file from a Directory/File Listener. It can also be from any of these protocols TCP/IP, HTTP or API. The HL7 message is routed to its destination based on MSH-6 (Receiving Facility) using the XPath expression. Before sending out the message, each of the Target transformation mappers are checked for the receiving application system name. Then, the name is changed to the destination’s application system name. After the transformation is complete, the HL7 message is sent out to each routing destination output file name and directory.
HL7 Message Routing:
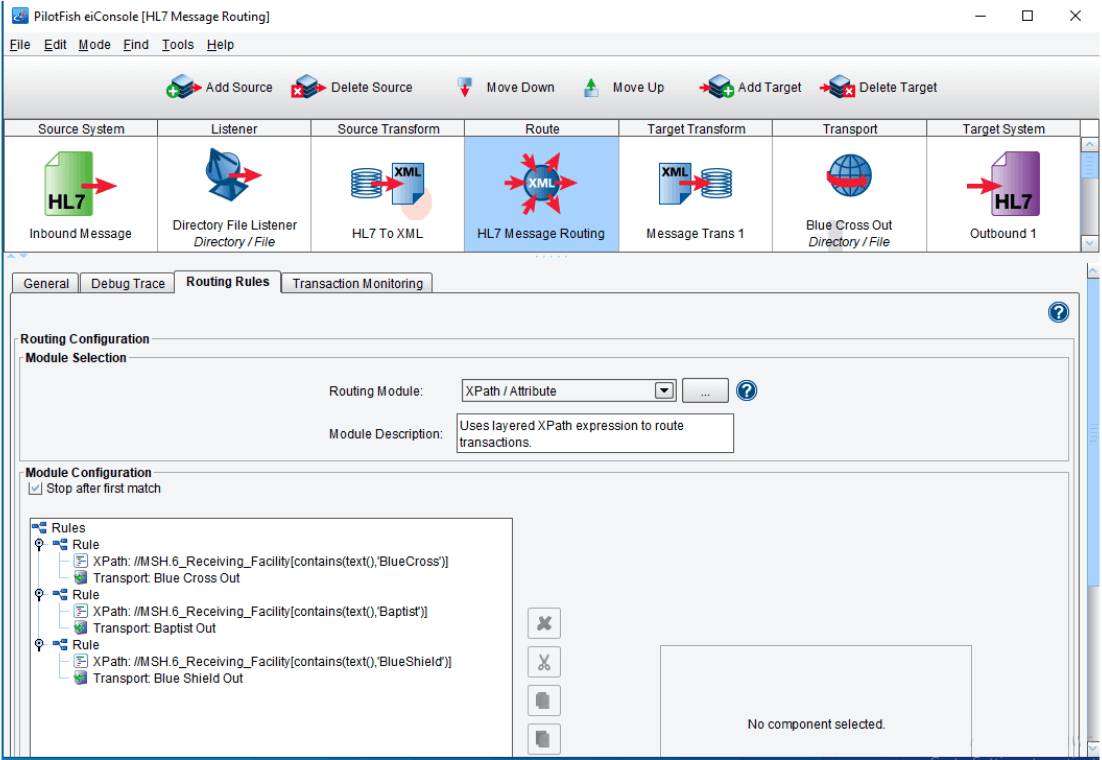
Using XPath to Create Routing Rules:
The example below shows that each message is routed based on MSH-6 (receiving facility). If the receiving facility is ‘BlueCross’, then it Routes the message to the Blue Cross Out transport. If the receiving facility is ‘Baptist’, then it routes the message to the Baptist Out transport. Finally, if the message is ‘BlueShield’, it routes the message to the Blue Shield Out transport.
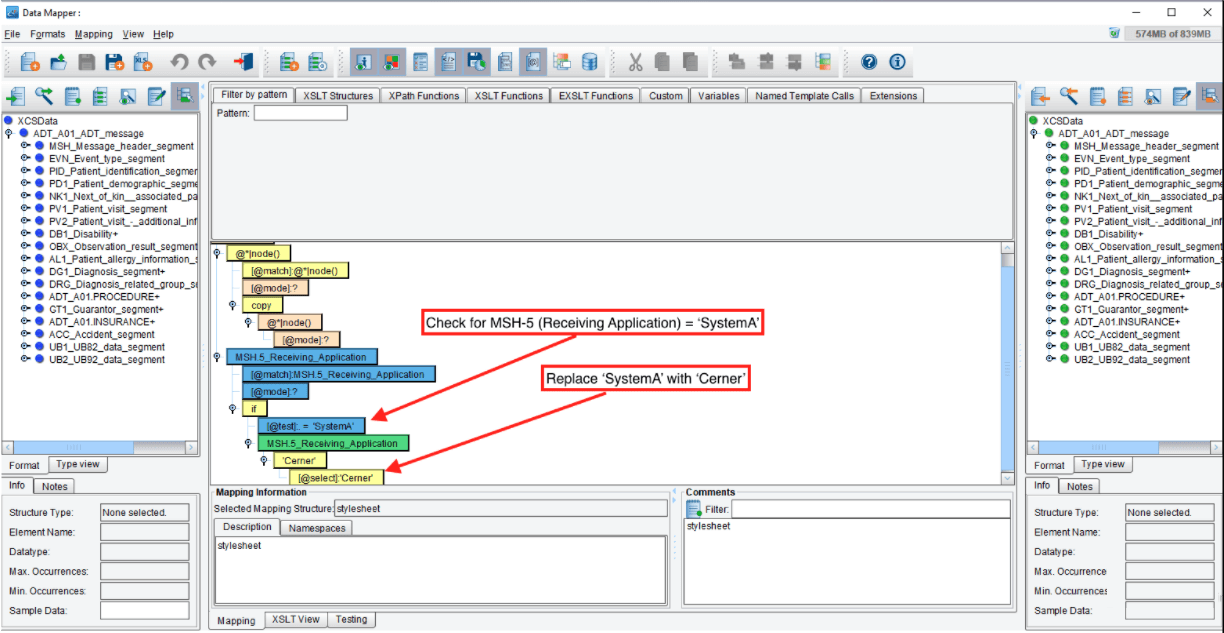
Target Transformation Mapper:
In each of the three Target transformations, the receiving application is mapped to the correct application system before the message is sent out. This example below checks for MSH-5 (Receiving Application) to see if the receiving application is ‘SystemA’, and if it matched, ‘Cerner’ is mapped to the receiving application field.
To test this route, we will be using a Directory/File Listener and poll for the files below from the ‘C:\PilotFish eiConsole Working Directories\data\In’.
- HL7RoutingFile1.txt
- HL7RoutingFile2.txt
- HL7RoutingFile3.txt
