Exercise 5.1 – A Simple Mapping
Purpose:
To practice building a simple XSLT mapping in the Data Mapper.
References:
Create a Route
- From the eiConsole File Management screen, select the Add Route button.
- In the dialog that appears, enter the name A Simple Mapping and select OK.
- The Route should now appear in the table on the screen. Double-click it to open it.
Document the Source System
- Select the Source System stage in the Route Editing Grid. The configuration panel will appear at the bottom.
- Change the System Name to Person XML File.
- Select the Choose Source Icon button, and scroll down to select one of the XML icons.
Configure the Listener
- Select the Listener stage in the Route Editing Grid. The configuration panel will appear at the bottom.
- Select Directory/File from the Listener Type selection box. Optionally, click the … button to open the Module Search Dialog, which provides a faster way to find the module you want.
- Assign a polling directory using the … button to open the file selector. The polling directory should NOT be the directory with all the sample files, since files will be moved/deleted by the Listening process.
- Go to the Post-Process tab and select Delete from Postprocess Operation.
Add Source Format and Open Data Mapper
- Select the Source Transform stage in the Route Editing Grid. The configuration panel will appear at the bottom.
- Click the Add Format button. In the dialog that appears, name the format Person to Robot, and click OK. The transformation configuration panel will appear below.
- On the right-hand side, in the XSLT To XML configuration panel, uncheck the Use Direct Relay button. The options in that panel will now be enabled.
- Click the New button beneath the checkbox to open the Data Mapper.
Load Source and Target Formats
- In the Data Mapper, make sure the tab at the very bottom of the screen that says Mapping is selected.
- There are 3 panels on the screen. The left-hand panel is for the Source Format, the right-hand panel is for the Target format, and the center panel is for the mapping.
- Above the Source format panel to the left is a row of buttons. Select the leftmost button from that row to open up the Select Format dialog.
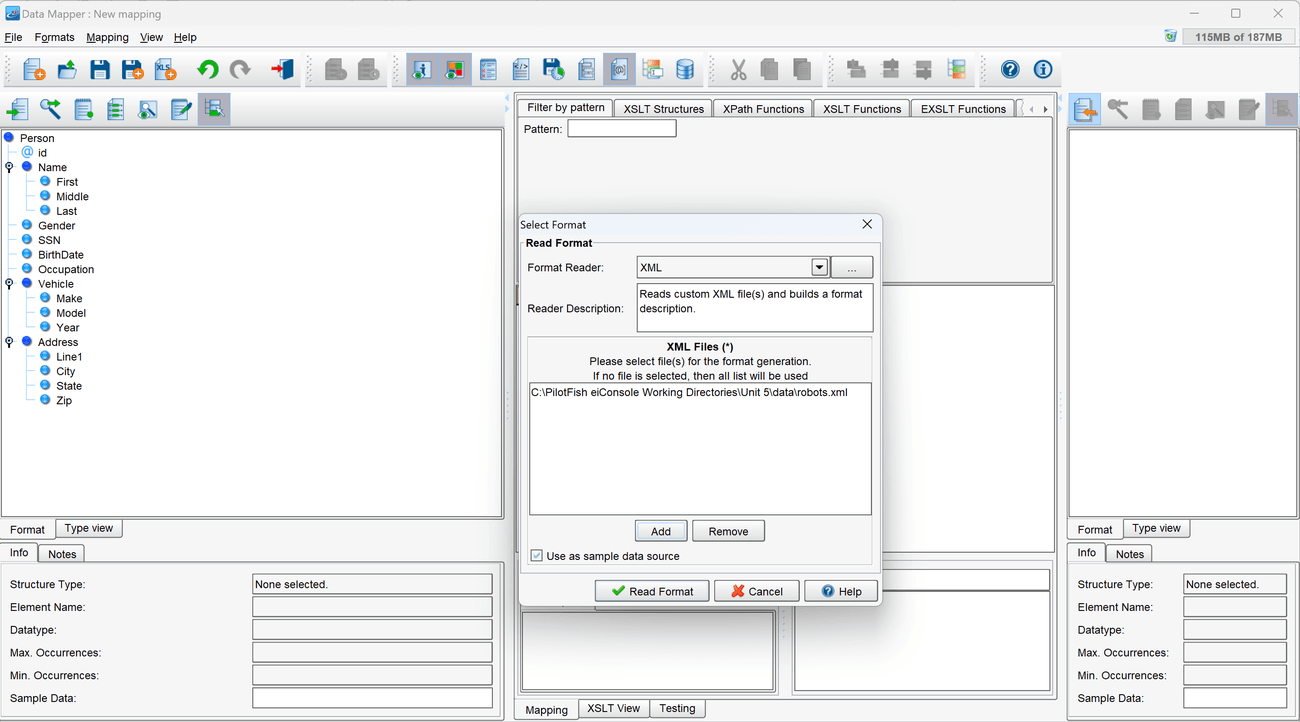
- Select XML from the Format Reader selection box. Optionally, click the … button to open the Module Search Dialog, which provides a faster way to find the module you want.
- In the configuration panel that appears, select the Add button. In the File Selector, navigate to the Sample Directory and select the file person.xml. Once it is selected, click Read Format.
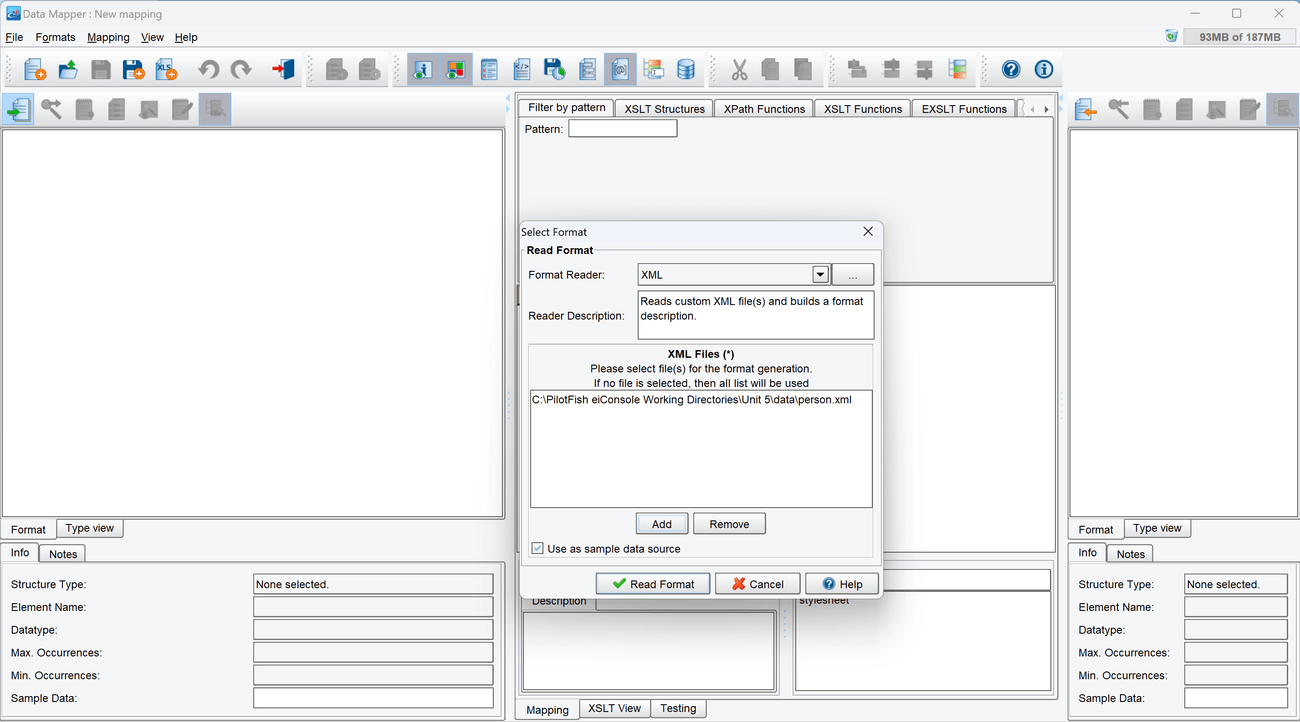
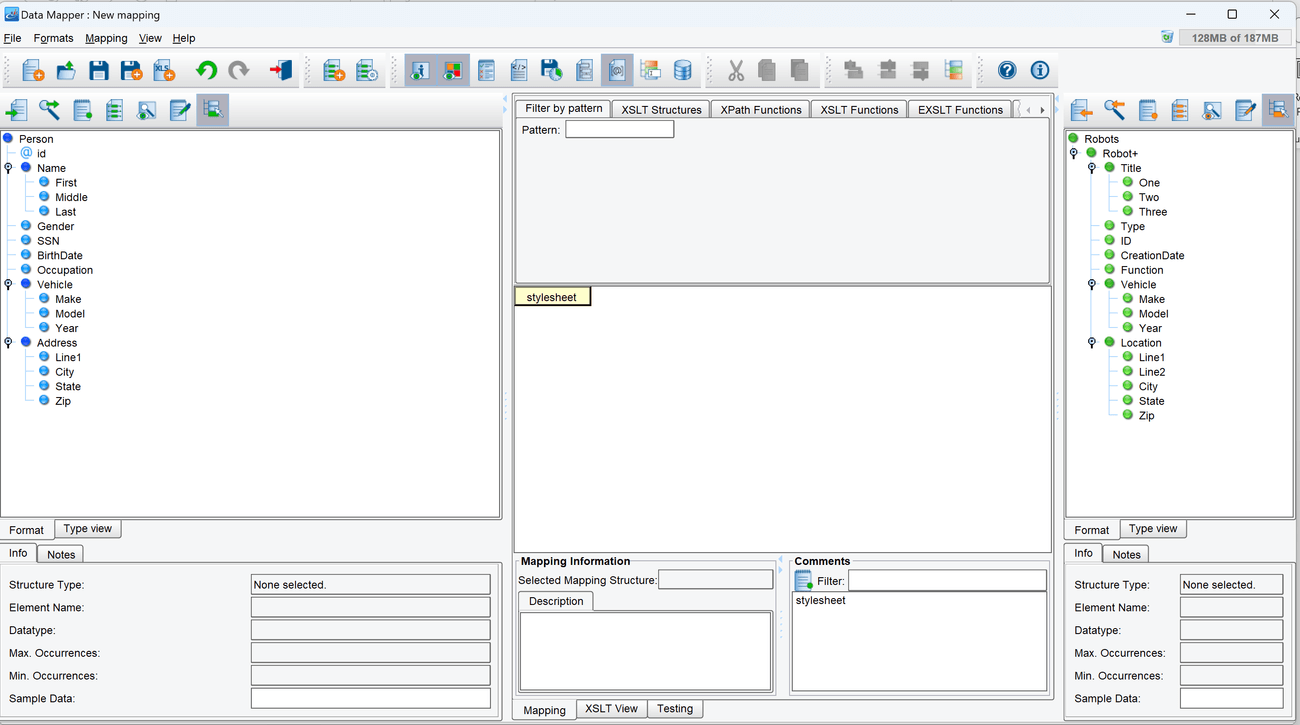
- The left-hand panel will now be populated with a blue-colored tree that represents the Source format.

- Above the Target format panel to the right, select the leftmost button from that row to re-open the Select Format dialog. Choose the XML option again from the Format Reader selection box.
- The previously selected file might still appear there. If it does, select it and then click the Remove button to erase it.
- Click the Add button and use the File Selector to navigate to the Sample Directory and select the file robot.xml. Once it is selected, click Read Format.

- The right-hand panel will now be populated with a green-colored tree that represents the Target format.

Perform Simple Mapping
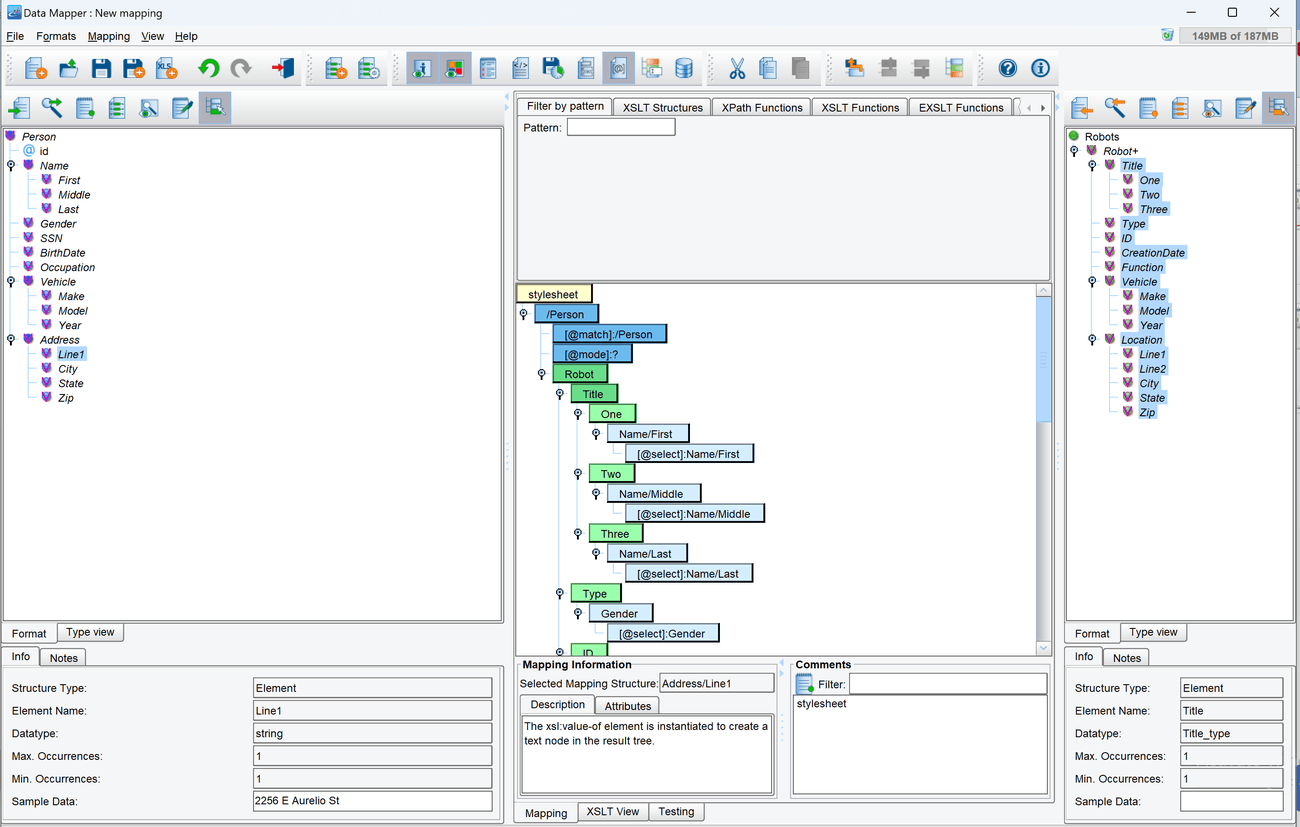
- Select the Person Node that is the root of the tree in the Source panel to the left. Drag it onto the center panel and drop it on the stylesheet node that’s already there.
- Select the Robot node that is the root of the tree in the Target panel to the right. Drag it onto the center panel and drop it on the Person node that was just dropped there. This completes the implicit default Template for the XSLT Stylesheet.
- Select all of the Nodes that are children of the Robot node in the Target format panel and drag them onto the center panel and drop them onto the Robot node.
- Click the + button next to the Title, Vehicle, and Location nodes in the Target format panel to expand them, which will show their child nodes.
- Select all the child nodes beneath Title in the Target format panel and drag them onto the center panel and drop them onto the Title node there. Repeat this with the children of Vehicle and Location.
- Now that the whole Target format has been configured in the center panel, it’s time to map the Source format to it. Map the nodes in the following way:
- Source: Name/First -> Target: Title/One
- Source: Name/Middle -> Target: Title/Two
- Source: Name/Last -> Target: Title/Three
- Source: Gender -> Target: Type
- Source: SSN -> Target: ID
- Source: BirthDate -> Target: CreationDate
- Source: Occupation -> Target: Function
- Source: Vehicle/Make -> Target: Vehicle/Make
- Source: Vehicle/Model -> Target: Vehicle/Model
- Source: Vehicle/Year -> Target: Vehicle/Year
- Source: Address/Line1 -> Target: Address/Line1
- Source: Address/City -> Target: Address/City
- Source: Address/State -> Target: Address/State
- Source: Address/Zip -> Target: Address/Zip

- Now that the mapping is complete, click the Save icon in the toolbar above the tree. When prompted for a name, use the default, transform.
- Click the X button in the top-right corner to close the Data Mapper and return to the Route Editing Grid.
Configure the Transport
- Select the Transport stage in the Route Editing Grid. The configuration panel will appear at the bottom.
- Select Directory/File from the Transport Type selection box. Optionally, click the … button to open the Module Search Dialog, which provides a faster way to find the module you’re looking for.
- Select the Target Directory, using the … button to open the file selector.
- Set robot-output as the Target File Name.
- Set xml as the Target File Extension.
Document the Target System
- Select the Target System stage in the Route Editing Grid. The configuration panel will appear at the bottom.
- Change the System Name to Robot XML File.
- Select the Choose Target Icon button and scroll down to select one of the XML icons.
Prepare to Test
- In the menu bar at the top, select Mode -> Testing Mode. Make sure the changes to the Route are saved.
- Copy the file called Person.xml from the Samples directory provided into the directory chosen as the polling directory.
Perform the Test
- At the top of the Testing Mode screen, select the Execute Test button.
- If the Route was configured successfully, all the Stages should light up with green checkmarks.
- In the OS File Explorer, open the directory selected as the Target Directory. The file robot-output.xml should be there, with the transformed contents produced by the XSLT.
Output Files
- Compare the results from the exercise with the following example output files to see if they are correct.