HTTP Form File Post Listener
In the eiConsole and eiPlatform, the HTTP Form File Post Listener monitors a specified local HTTP path for POST requests with ‘File’ attachments. The attachment is used as input data.
Select the HTTP Form File Post Listener from the Listener Type drop-down.
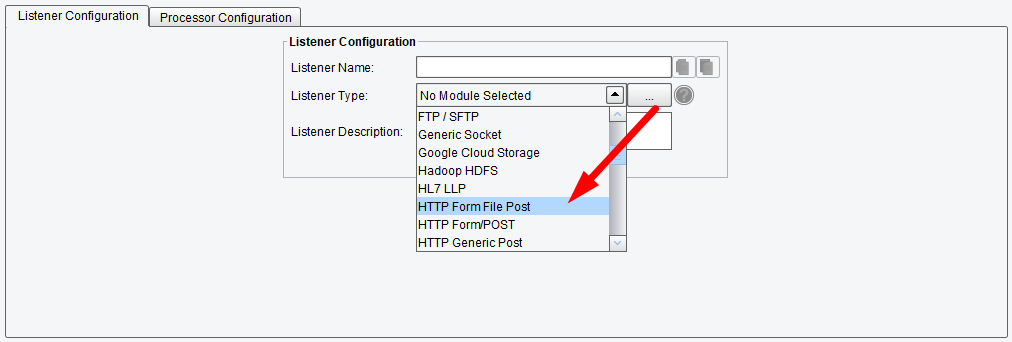
Listener (Adapter) Configuration Drop-Down List
Basic HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
This Listener has 8 tabs: Basic, Advanced, Transaction Logging, Inactivity, Throttling, WSDL, Authentication, and Resources.
On the Basic tab you can specify:
- Request path – specifies the HTTP path to listen to, modified by the application server
- Timeout – specifies how long the Listener should wait for messages which are interrupted before timing out the connection
- WSDL File – WSDL file that would be returned on request that ends with “?wsdl”. If you want to create new or edit existing files, you can click Edit/New to open the WSDL editor.

HTTP Form File Post Listener Basic Configuration Options
Advanced HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
The Advanced tab allows you to specify whether or not it should run only when the Listener is triggered externally and how many elements should be serialized.
Also, you can configure the following options:
- Allow Command-Line Invocation – if enabled, the listener can be invoked using the CLI client application
- Restart on Listening Error – if enabled, the listener will be restarted after an error occurs
- FIFO Queue Name – the FIFO options enable a “First In, First Out” queuing mechanism between Listeners and Transports. If a FIFO Queue Name is provided, it will be used as a key for a transaction queue. Transactions will be written to this queue before they reach a Transport. The transactions in this queue will be ordered according to when they were created by the Listener.
- FIFO Queue Delay – this is the interval between updates or checks against that queue. Providing a queue name guarantees that a given Transport sends transactions in the same order that the Listener created them in.
- Synchronous – specifies whether or not a response is expected
- Require SSL – if selected, plain text requests will be rejected
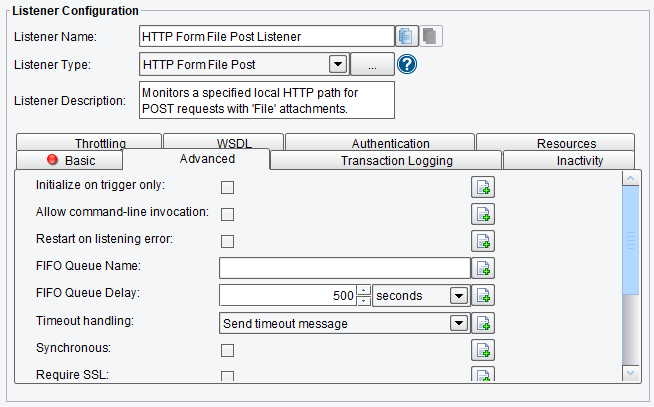
HTTP Form File Post Listener Advanced Configuration Options (top half of screen)
- HTTP Headers – allows specification of HTTP header name-value pairs to use in synchronous response

HTTP Form File Post Listener Advanced Configuration Options (bottom half of screen)
Transaction Logging HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
The Transaction Logging tab allows you to specify:
- Transaction Logging Enabled – if enabled, allows transaction events originating from this Listener to be logged by a TransactionEventListener
- Log Transaction Data – if enabled, logs transaction data body
- Log Transaction Data Base64 – if enabled, logs transaction data body as Base64
- Log Transaction Attributes – if enabled, logs transaction attributes
- Log All Attributes – if enabled, no attributes will be filtered
- Allowed Attributes – attributes that are allowed to be logged

HTTP Form File Post Listener Transaction Logging Configuration Options
Inactivity HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
The Inactivity tab allows you to specify:
- Enable Inactivity Monitor – check this box to enable inactivity monitoring. This will throw a non-transaction exception if the specified number of transactions haven’t been processed in the specified time interval.
- Min. Transactions to Expect – the number of transactions to expect to be completed per monitoring interval
- Monitoring Interval – how often to check the specified number of transactions that have been processed
- Times to Monitor – if set, monitoring will be done during the defined times of the day. To ignore, set start and end time equally.
- Days to Exclude from Monitoring – inactivity monitoring will not occur on the days specified
- Include Errors in Transaction Count – if checked, transactions that attempted to start, but failed at the Listener stage, will also be counted

HTTP Form File Post Listener Inactivity Configuration Options
Throttling HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
The Throttling tab allows you to specify:
- Throttling Mode – the throttling mode to use for limiting the number of transactions or messages emitted by this Listener. “Timed” will limit transactions based on time intervals, while “Concurrent” will limit based on a concurrent number of transactions. “Concurrent” mode requires a Throttling Response Processor step later in your interface workflow to acknowledge completion.
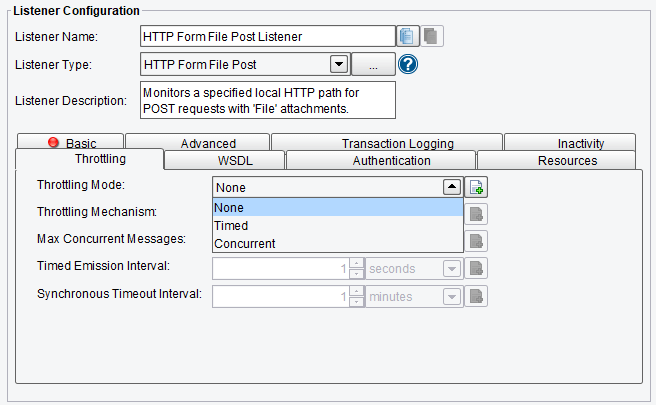
HTTP Form File Post Listener Throttling Mode
- Throttling Mechanism – the mechanism to use for throttling messages. “Blocking” prevents the Listener from continuing to process and emit messages altogether, while “queued” pushes received messages into the interface queue or a default, in-memory queue.
- Max Concurrent Messages – how many messages can be concurrently processed, either by time-based limits (allow X per second) or synchronous (allow X at any time)
- Timed Emission Interval – the interval for time-based limits (allow X per X timed emission interval)
- Synchronous Timeout Interval – the interval to wait for a synchronous response before failing
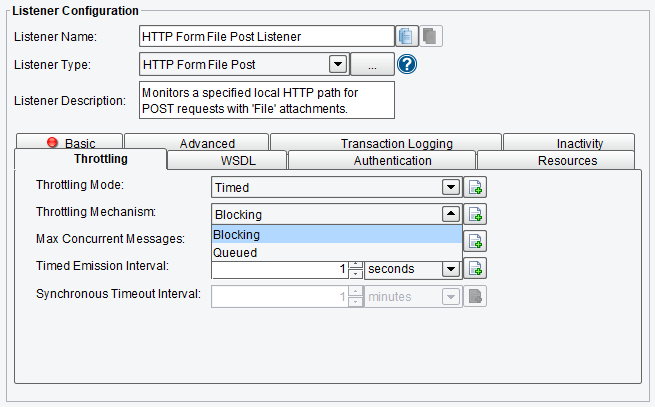
HTTP Form File Post Listener Throttling Configuration Options
WSDL HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
On the WSDL tab you can specify:
- WSDL Content Type – specifies the content type to send with the WSDL file
- Validate At The Listener Level – if selected, the Listener will validate incoming message against XML schema in defined WSDL

HTTP Form File Post Listener WSDL Configuration Options
Authentication HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
On the Authentication tab you can specify usage of Basic Authentication:
Also, you can set:
- Authentication File – a properties file containing usernames and passwords for basic authentication
- Authentication Realm – the realm for basic authentication
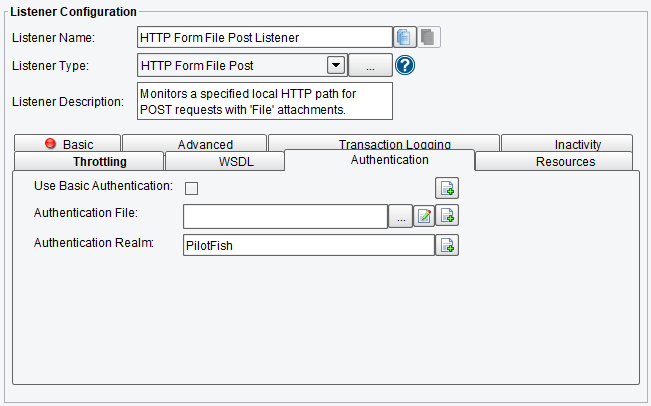
HTTP Form File Post Listener Authentication Configuration Options
Resources HTTP Form File Post Listener Configuration Options
On the Resources tab you can specify:
- Additional Resources – specifies any additional content to be served up and the URL fragment at which they are served up
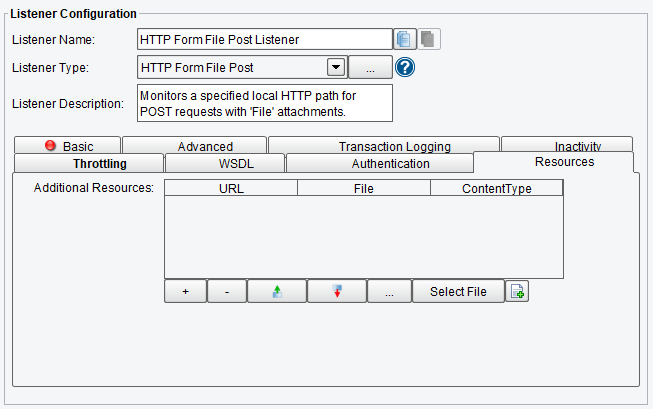
HTTP Form File Post Listener Resources Configuration Options
