Document-Style Web Service Listener
This Listener allows you to take a data stream in through a WSDL defined Web Service, which includes one method that accepts all of the inbound data as a single string parameter. This is the simplest way to implement a WSDL defined Web Service.
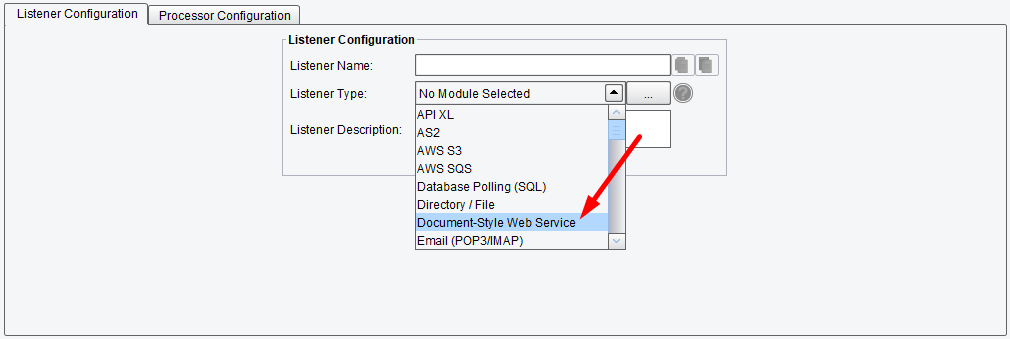
Listener (Adapter) Configuration Drop-Down List
Basic Document-Style Web Service Listener Configuration Options
First, the Basic tab allows you to specify the following:
- Service Name – this is used to differentiate this Web Service against others in the system.
- Axis URL – Web Services are deployed using the Apache Axis platform. In cases where the Axis URL cannot be discovered automatically by the eiPlatform, you can enter the URL directly. This is typically not required.
- Allowed Methods – this line will list the allowed platforms. To edit this, choose the icon to the right of the line.
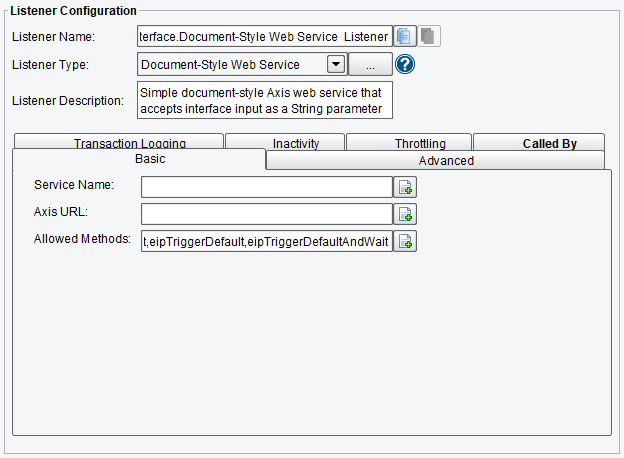
Document-Style Web Service Listener Basic Configuration Options
Advanced Document-Style Web Service Listener Configuration Options
The Advanced tab lets you specify the port on which the admin service is running, as well as if this Listener should be initialized only when it is triggered from an external source.
- Initialize on Trigger Only – if enabled, the Listener doesn’t start up until a trigger initializes it
- Allow Command-Line Invocation – if enabled, the listener can be invoked using the CLI client application
- Restart on Listening Error – if enabled, the listener will be restarted after an error occurs
- FIFO Queue Name – The FIFO stuff enables a “First In, First Out” queuing mechanism between Listeners and Transports. If a “FIFO Queue Name” is provided, that name will be used as a key for a queue Transactions & will be pushed into before reaching a transport. They’ll be ordered in this queue according to when the Listener created them.
- FIFO Queue Delay – It is the interval between updates/checks against that queue. Providing a queue name guarantees that a given Transport sends transactions in the same order that the Listener created them in.
- Port – specifies the port to listen at: 8080 by default

Document-Style Web Service Listener Advanced Configuration Options
Transaction Logging Document-Style Web Service Listener Configuration Options
The Transaction Logging tab allows us to enable transaction events logging. That data can be logged by a TransactionEventListener.
- Transaction Logging Enabled – this checkbox allows transaction events originating from this Listener to be logged by a TransactionEventListener
- Log Transaction Data – if enabled, logs transaction data body
- Log Transaction Data Base64 – if enabled, logs transaction data body as Base64
- Log Transaction Attribute – if enabled, logs transaction attributes
- Log All Attributes – if enabled, no attributes will be filtered
- Allowed Attributes – attributes which are allowed to be logged

Document-Style Web Service Listener Transaction Logging Configuration Options
Inactivity Document-Style Web Service Listener Configuration Options
On the Inactivity tab, you are allowed to specify:
- Enable Inactivity Monitor – Check this box to enable inactivity monitoring. This will throw a non-transaction exception if the specified number of transactions haven’t been processed in the specified time interval.
- Min. Transactions to Expect – the number of transactions to expect to be completed per monitoring interval
- Monitoring Interval – how often to check the specified number of transactions that have been processed
- Times to Monitor – if set, monitoring will be done during the defined times of the day. To ignore, set start and end time equally.
- Days to Exclude from Monitoring – inactivity monitoring will not occur on the days specified
- Include Errors in Transaction Count – if checked, transactions that attempted to start, but failed at the Listener stage, will also be counted
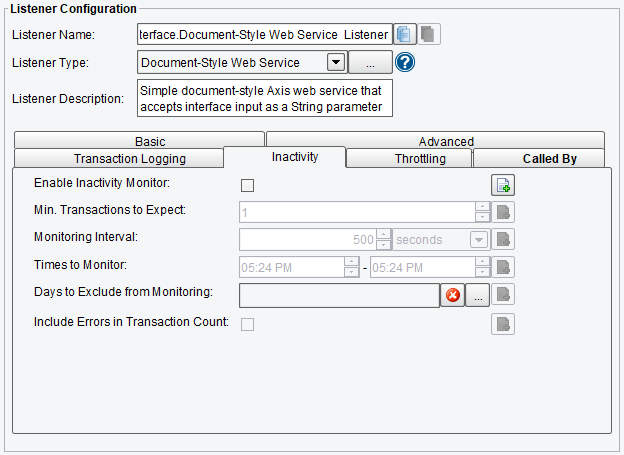
Document-Style Web Service Listener Inactivity Configuration Options
Throttling Document-Style Web Service Listener Configuration Options
On the Throttling tab, you are allowed to specify:
- Throttling Mode – the throttling mode to use for limiting the number of transactions or messages emitted by this Listener. “Timed” will limit transactions based on time intervals, while “Concurrent” will limit based on a concurrent number of transactions. “Concurrent” mode requires a Throttling Response Processor step later in your interface workflow to acknowledge completion.

Document-Style Web Service Listener Throttling Mode
- Throttling Mechanism – the mechanism to use for throttling messages. “Blocking” prevents the Listener from continuing to process and emit messages altogether, while “Queued” pushes received messages into the interface queue or a default, in-memory queue.
- Max Concurrent Messages – how many messages can be concurrently processed, either by time-based limits (“Allow X per Second”) or synchronous (“Allow X at any Time”)
- Timed Emission Interval – the interval for time-based limits (“Allow X per X Timed Emission Interval”)
- Synchronous Timeout Interval – the interval to wait for a synchronous response before failing
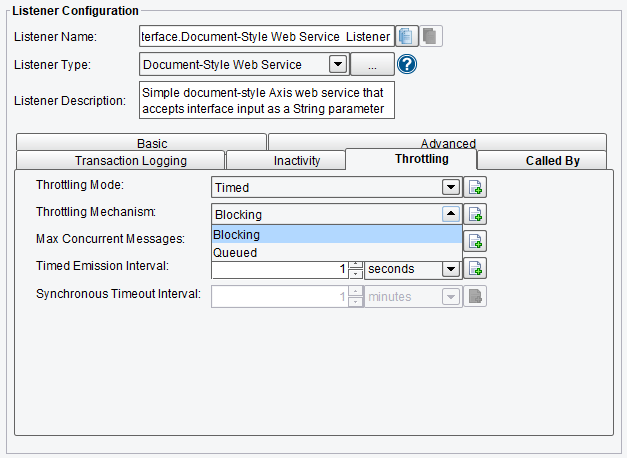
Document-Style Web Service Listener Throttling Configuration Options
Called By Document-Style Web Service Listener Configuration Options
The Called By tab allows you to check if the current Route is called by a RouteToRoute Transport and if so, by which one.
- Called By – the Routes called into this listener (if there are any)
Document-Style Web Service Listener Called By Configuration Options
